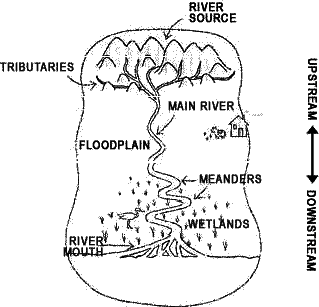
- Explain the difference between the upper course, middle course and lower course of a river.
- Where is the place to erosión? , and to the deposition of sediments?
- What types of reliefs are possible in these areas? Look for information here and in your book, page 42

Complete the table:
| Course of a river | ||
| Parts | Where? | Main features |
| Upper | ||
| Middle | ||
| Lower | ||